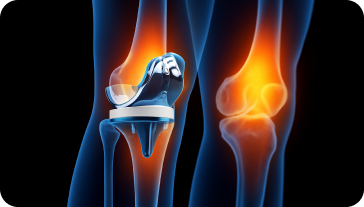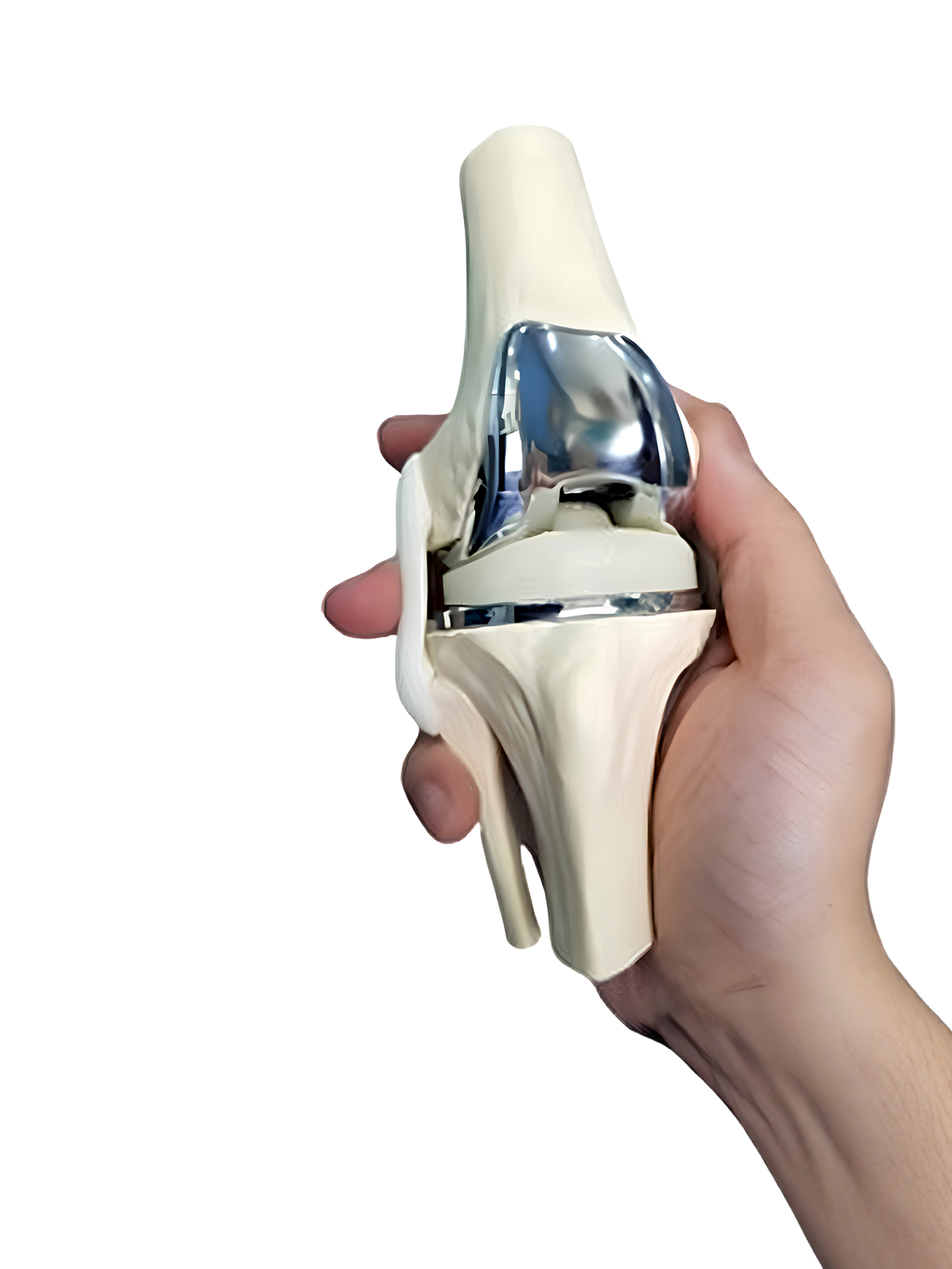
When is Knee Replacement Surgery Recommended?
- Chronic knee pain that limits daily activities
- Severe osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis
- Knee deformities such as bowing in or out
- Stiffness and swelling that does not improve with medications
- Failure of previous knee treatments, including physical therapy and injections
Benefits of Knee Replacement Surgery
- Pain Relief: Significant reduction in chronic knee pain
- Improved Mobility: Restores the ability to walk, climb stairs, and perform
daily activities - Enhanced Quality of Life: Increases independence and overall
well-being - Durable Results: Modern knee implants last 15–20 years with
proper care
Recovery After Knee Replacement
Surgery
- Hospital Stay and Immediate Post-Op Care
Most patients stay in the hospital for 2–4 days. Pain management,
blood clot prevention, and mobility exercises start immediately. - Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation begins within 24 hours of surgery. A physiotherapist
will guide you through gentle exercises to restore knee function. - Home Care and Long-Term Recovery
Follow a balanced diet to promote healing.
Use a walker or crutches initially for support.
Avoid high-impact activities and follow-up regularly with your doctor.
Types of Knee Replacement Surgery
Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
The most common procedure where the entire knee joint is replaced with a prosthetic implant, suitable for patients with severe arthritis affecting the whole knee.
Partial Knee Replacement (PKR)
Partial knee replacement is performed when only one part of the knee is damaged. This procedure preserves more natural bone and tissue, leading to quicker recovery.
Bilateral Knee Replacement
In cases where both knees are severely affected, bilateral knee replacement surgery is performed either simultaneously or in stages.
Minimally Invasive Knee Replacement
This advanced technique uses smaller incisions, leading to reduced pain, minimal scarring, and a shorter hospital stay
The Knee Replacement Procedure
Anesthesia
The procedure is performed under either general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia, depending on the patient's health.
Incision & Joint Removal
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia or spinal anesthesia with sedation.
Implant Placement
Artificial knee components made of metal or plastic are placed and secured using surgical cement or press-fit techniques.
Closure & Recovery
The incision is closed using sutures or staples, and the knee is bandaged to prevent infection.
How to Ensure a Successful Knee Replacement Recovery
1. Follow Post-Surgical Instructions
Take prescribed medications as directed.
Attend all follow-up appointments.
2. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Maintain an ideal weight to reduce stress on the knee joint.
Stay active with low-impact exercises like swimming and cycling.
3. Engage in Regular Physiotherapy
Perform recommended exercises to regain strength.
Avoid activities that put excessive strain on the knee.